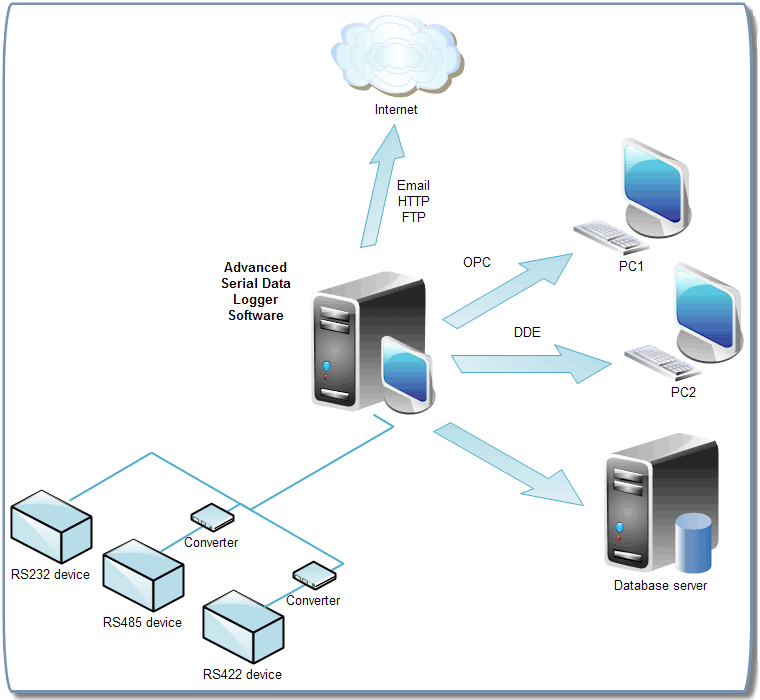
DATA COMMUNICATIONS
Types of communication :
Any communications channel has a direction associated with it:
The message source is the transmitter, and the destination is the receiver. A channel whose direction of transmission is unchanging is referred to as a simplex channel. For example, a radio station is a simplex channel because it always transmits the signal to its listeners and never allows them to transmit back.
The basic components of data communications are:
Sending device ->
NETWORK
è Series of points or nodes interconnected by communication paths. Networks can interconnect with other networks and contain subnetworks.
- LAN
LANs (local area networks) are networks that connect computers and resources together in a building or buildings close together.
- MAN
Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) are networks that connect LANs together within a city.
- WAN
Wide Area Networks (WANs) connect LANs together between cities.
Network topology
- Bus Network
- each node is connected to a single cable.
- A signal from the source travels in both directions to all machines connected on the bus cable until it finds the intended recipient.
- If the machine address does not match the intended address for the data, the machine ignores the data. Alternatively, if the data does match the machine address, the data is accepted.
- it is rather inexpensive to implement when compared to other topologies. However, the low cost of implementing the technology is offset by the high cost of managing the network. Additionally, since only one cable is utilized, it can be the single point of failure If the network cable breaks, the entire network will be down.
- Star Network
- Each network host is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection.
- All traffic that traverses the network passes through the central hub. The hub acts as a signal repeater.
- The star topology is considered the easiest topology to design and implement.
- An advantage of the star topology is the simplicity of adding additional nodes.
- The primary disadvantage of the star topology is that the hub represents a single point of failure.
- Ring Network
Communications Devices
- A network topology that is set up in a circular fashion in which data travels around the ring in one direction and each device on the right acts as a repeater to keep the signal strong as it travels.
- Each device incorporates a receiver for the incoming signal and a transmitter to send the data on to the next device in the ring.
- The network is dependent on the ability of the signal to travel around the ring
- Communications devices
- Communications Devices is any type of hardware capable of transmitting data, instructions, and information between devices.
- Dial-up modem
- Dial-up modem is convert digital signals to analog and vice versa.
- Notebook computers often use PC Card modem.
- Cable modem
- Sends and receives data over cable television network.
- Much faster than dial-up modem or ISDN.
- Wireless modem
- Allows access to the Web wirelessly from a notebook computer, a PDA, a smart phone, or other mobile device.
- Typically use the same waves used by cellular telephones.

- Network Card
- Adapter Card,PC Card, Express Card module, USB network adapter or flash card that enables a computer or devices to access network.

- Wireless Access Point
- Central communication device that allows computers and device to transfer data wirelessly among themselves or to wired network.

- Router
- Connect computers and transmits data to connect destination on network
- Router forward data on the Internet using fastest available path

COMMUNICATION MEDIA
- Wire pair/Twisted pair
- The most communication media
- Wire pairs are inexpensive
- Coaxial cable
- Known for sending a strong signal
- coaxial cables has much higher bandwidth

- Fiber Optic
- Fiber optics use light and the cables are made of glass or plastic fibers, each thinner than a human hair
- Fiber optics cables has a much higher bandwidth than coaxial cables, yet less expensive
- It uses light rather than electricity

- Microwave transmission
- Use as line-of-sight transmssion of data signals via atmosphere.
- Often antennas in high places, such as the tops of mountains and buildings-positioned at point as approximately 30 miles apart to continue the transmission.
- Microwave transmission offers high speed, cost-effectiveness and ease implementation.
- One problem is susceptibility to interference by whether conditions.
- Satellite transmission
- Satellite transmission is a form of microwave transsmission in which a satellite acts as the relay station.
- Its basic component are earth stations, which send and receive signals.
- Transponder is the satellite components that receive the transmission from an earth.
- This entire process takes only a fraction of a second.
- Wireless transmission
- Wireless transmission is a group of technologies has recently emerged that transmit data over relatively short distances.
- IrDA uses infrared to transmit data a few feet between devices, such a PDA and a desktop or a computer and a printer.
- Similar to TV remote, IrDA requires a direct line-of-sight.
- Bluetooth is another short distance technique(30 feet or less) that uses radio waves to connect mobile devices such as handhelds, notebooks and cell phones.
- Wi-fi (wireless fidelity) is a standard uses for distance up to about 150 feet.
- Wi-fi capability is built into some notebook model, allowing them to easily join wireless LANs.
- 802.11a and 802.11g are the newest members of this family and allow transmission at speeds up to 54 Mbps.
BITS AND BYTE
- Bit
- Short for binary digit.
- Two possible value : 0 and 1
- Can never be empty
- Basic unit for storing data.
- 0 means off, 1 means on.
- Byte
- A group of 8 bits
- Each bit has 256 (28) possible values.
- For text, stores one character
- Can be letter, digit or special character
- Memory and storage devices measured in number of byte.










0 comments:
Post a Comment